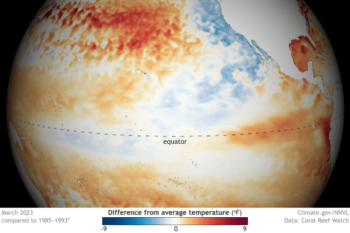
El Niño is returning this year, with significant effects expected for our weather in 2023. El Niño’s return comes after three straight years of La Niña conditions in the tropical Pacific, what climatologists call a “triple dip.” Typically events last less than a year: this La Niña event started in July 2020 and is only coming to an end now.
So what is El Niño? That’s what this article will attempt to answer. Below, we delve into the intricacies of El Niño and La Niña, discuss their impacts on US weather, and help our readers understand the differences between these two significant climate events.
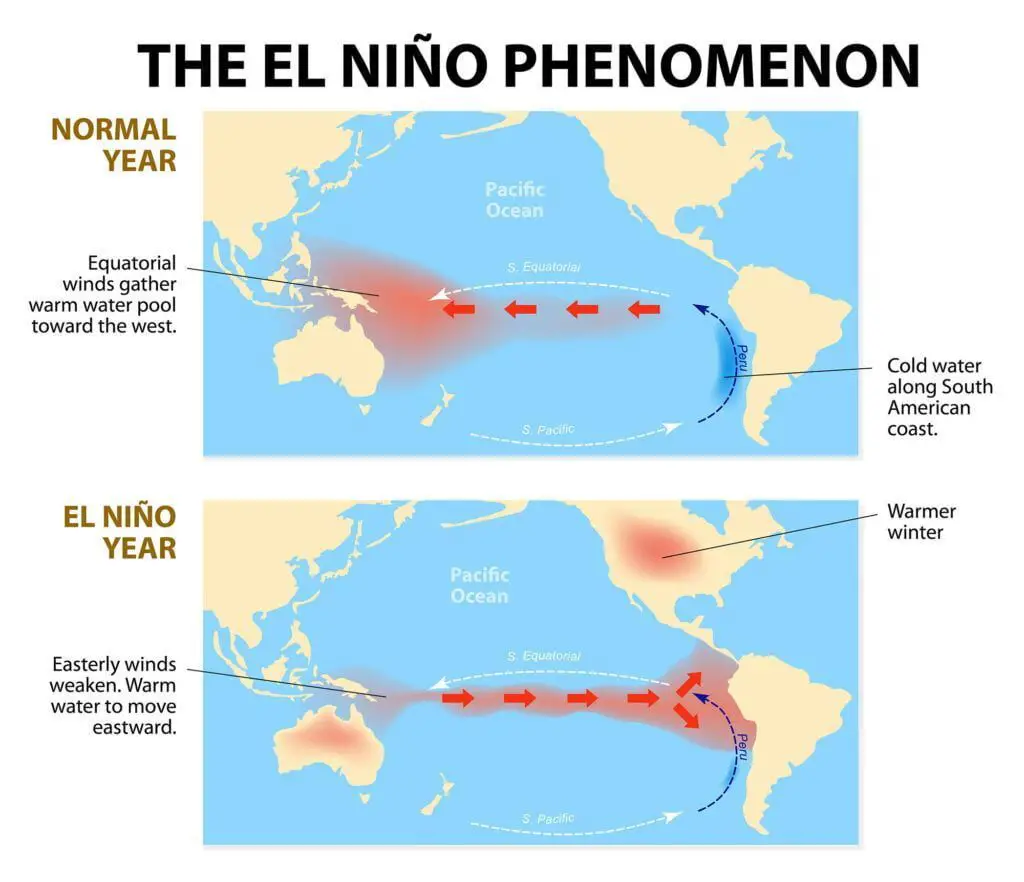
What is El Niño (and La Niña)?
El Niño and La Niña are two phases of the El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) cycle, a climate pattern in the tropical Pacific Ocean. Unusually warm ocean surface temperatures characterize El Niño, while La Niña features cooler-than-average temperatures in the same region. These temperature fluctuations result from complex interactions between the ocean and atmosphere, including changes in trade winds, ocean currents, and the jet stream. The formation of both El Niño and La Niña events can lead to significant changes in global weather patterns.
There is also the natural phase, sometimes unofficially labeled “La Nada.” Here, sea surface temperatures are close to normal, and there are little, if any, effects on the weather patterns globally (however, other climate cycles can have outsized roles in the weather patterns here in the States as a result!).
The ENSO cycle typically lasts two to seven years, with El Niño and La Niña events alternating irregularly. In some cases, as has just happened, events of the same type can follow one another. The strength of these events varies, and their impacts can differ accordingly. Although predicting the exact timing and intensity of El Niño and La Niña events remains a challenge for meteorologists, advancements in climate modeling have improved our ability to forecast their onset and duration.
[embedyt] https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=d6s0T0m3F8s[/embedyt]What Causes El Niño and La Niña to happen?
The interactions between the ocean and atmosphere in the tropical Pacific Ocean primarily drive El Niño and La Niña events. Several factors influence the ENSO cycle, including ocean surface temperatures, trade winds, and atmospheric pressure.
- Ocean surface temperatures: The ocean surface temperatures in the tropical Pacific play a significant role in determining the phase of the ENSO cycle. During El Niño events, the ocean surface temperatures in the central and eastern Pacific are warmer than average, while during La Niña events, they are more relaxed. These temperature anomalies can impact atmospheric circulation and weather patterns across the globe.
- Trade winds: Trade winds are a key factor in developing and maintaining El Niño and La Niña events. The trade winds blow from east to west across the tropical Pacific, pushing warm surface waters westward and allowing cooler water to rise from the depths in the east. During El Niño events, these trade winds weaken or reverse, accumulating warm water in the eastern Pacific. Conversely, during La Niña events, the trade winds strengthen, causing cooler water to rise to the east and central Pacific surface.
- Atmospheric pressure: The Southern Oscillation, a seesaw atmospheric pressure pattern between the eastern and western tropical Pacific, is closely linked to the ENSO cycle. During El Niño events, atmospheric pressure is typically lower over the eastern Pacific and higher over the western Pacific, while during La Niña events, the pressure pattern is reversed. These pressure changes can further influence the strength and direction of trade winds, leading to a feedback loop that helps maintain El Niño and La Niña conditions.
It’s important to note that the factors mentioned above are crucial drivers of the ENSO cycle. These precise mechanisms that trigger the onset of El Niño and La Niña are still not completely understood. However, ongoing research and advances in climate modeling continue to improve our understanding of these complex climate phenomena and their impacts on global weather patterns.

What is El Niño’s Effect on US Weather?
While it can affect weather year-round, El Niño effects are most pronounced in the winter months in the US (and conversely, the summer in the Southern Hemisphere).
During El Niño events, the United States generally experiences warmer-than-average temperatures across the northern states and cooler temperatures in the southern states during winter. This is due to the jet stream’s shift, which results in a more direct flow of moist, warm air from the Pacific Ocean across the country. The altered jet stream can also change the frequency and intensity of storms, potentially increasing the risk of severe weather events.
Precipitation patterns also change during El Niño events, with increased rainfall typically seen along the country’s southern tier while drier conditions prevail in the northern states. These changes in precipitation can result in flooding in some regions and droughts in others. Additionally, El Niño events may influence the development of tropical storms and hurricanes in the Atlantic Ocean in the Summer, with a tendency toward fewer storms during El Niño years.
Notable past El Niño events, such as the 1997-1998 and 2015-2016 events, led to significant disruptions in US weather patterns, including severe storms, flooding, and widespread drought. The impacts of El Niño events can vary in severity and duration, with some episodes causing more substantial disruptions than others.
La Niña events are different and commonly the reverse. Winters are colder and wetter in the north and warmer and drier in the south, with a noted increase in Atlantic tropical activity during the summer.
Getting Ready
The importance of weather forecasts and monitoring during El Niño events cannot be overstated. Accurate predictions and early warnings can help mitigate the potential consequences of these events, such as the disruption of agriculture, infrastructure, and public safety. Government agencies, meteorological organizations, and private weather forecasting companies all play a vital role in monitoring and predicting the impacts of El Niño events on US weather.
Individuals and communities should also prepare for El Niño-related weather events. This includes staying informed about weather forecasts, creating emergency plans for floods or severe storms, and taking precautions to protect homes and property from potential damage. By understanding the potential impacts of El Niño events and being prepared, we can better adapt to the challenges posed by these complex climate phenomena.
Wrapping Up
El Niño and La Niña events significantly impact US weather patterns, with each phase of the ENSO cycle producing distinct temperature and precipitation changes. By understanding what is El Niño and La Niña, and staying informed about their potential impacts, individuals and communities can better prepare for the challenges they may bring.