In recent years, the term “polar vortex” has rapidly transformed from a technical meteorological term to a widely recognized phrase in our winter vocabulary. Its mention often evokes a sense of dread as images of frigid temperatures come to mind. However, not everything you’ve heard about the polar vortex is accurate. This article aims to break down the facts about the polar vortex, explain its behavior, and debunk some common misconceptions.
We also have this blog post in video form, in case you’re in a hurry.
What is the Polar Vortex?
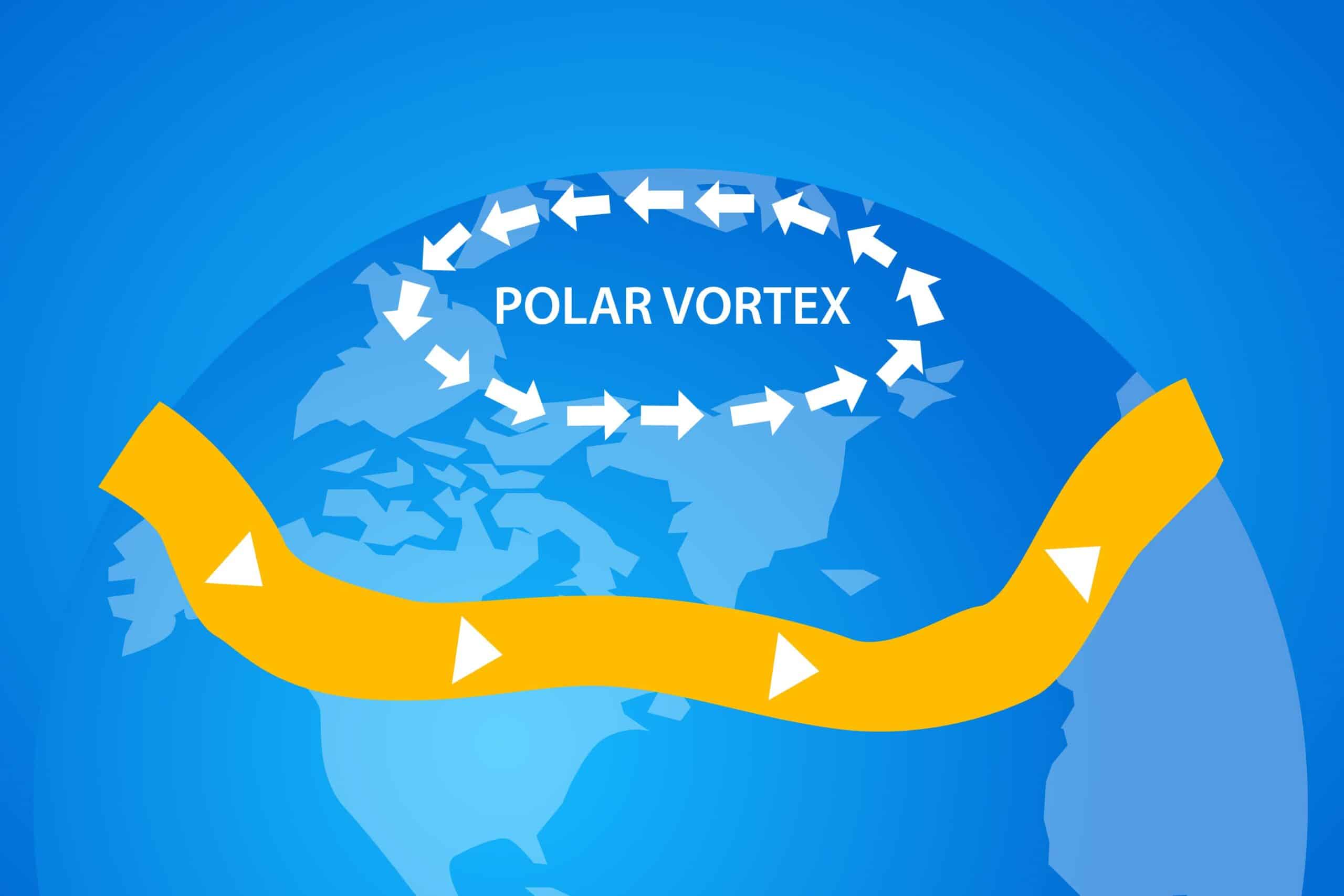
At its core, the polar vortex is not a new science. It refers to areas of low pressure rotating around the Earth’s poles, usually trapping the coldest air within the Arctic during the winter months. However, this system can sometimes be interrupted by an event called “sudden stratospheric warming.”
These sudden warming events might sound alarming, but they’re fairly common occurrences in the atmosphere. They happen when the stratosphere—the layer of Earth’s atmosphere above the troposphere—warms unexpectedly. This warming weakens the stratospheric polar vortex and, in some instances, reverses the direction of the westerly winds that encircle the poles.
(Note that in the troposphere, winds at the poles traditionally blow from the east – i.e. the Polar Easterlies, the opposite of the stratosphere.)

Classification of Warming Events
Scientists categorize warming events into two types: minor and major. During a minor event, the typical westward blowing winds at the poles weaken but don’t completely reverse. As a result, the polar vortex remains mostly intact, which limits its impact to higher latitudes.
Major events, on the other hand, present a different scenario. Here, the polar winds not only weaken but can sometimes reverse entirely. This phenomenon can disrupt the polar vortex, occasionally splitting it into two, which affects weather patterns in the mid-latitudes where most of us live. It often results in extremely cold weather.
While minor events happen several times annually, major events are less frequent, typically occurring once every couple of years. On very rare occasions, more than one major event can happen in a single season, leading to historically low temperatures.

Weather Predictions: Separating Fact from Speculation
It’s important to take online forecasts and videos with a grain of salt. While we have a foundational understanding of the polar vortex, predicting how it influences surface weather, especially during less intense disturbances, remains challenging.
Most major disruptions force Arctic air into regions like Siberia and can extend into North America and Northern Europe. This generally leads to very cold, dry conditions in the U.S., while Northern Europe experiences increased precipitation and potential snowstorms. However, not every major event guarantees these conditions.
The limitations of current weather models, which struggle to simulate the stratosphere accurately compared to surface conditions, further complicate predictions. Given that stratospheric warming was only identified in the 1950s, the available data for forecasting these events remains limited.
The polar vortex may be on its way, bringing the chill, but that doesn’t mean we can’t find ways to enjoy it. Whether it’s engaging in fun winter activities or simply catching up on things you’ve postponed, there’s plenty to do during cold spells. For us, it’s an ideal time to create more informative content that you’ll appreciate.
As the polar vortex descends, remember to stay warm and informed. Equip yourself with the facts over the hype, and enjoy the winter season responsibly.
Editor’s note: A previous version of our article included several inaccuracies which we were not aware of until we published our video. We have corrected our blog post and regret the error.